Intrapreneurship, a concept revolutionizing the traditional corporate landscape, is not just a buzzword but a beacon guiding organizations toward a culture of innovation and growth. Intrapreneurship goes beyond the routine. It’s about empowering employees to be architects of change, instilling an entrepreneurial mindset within the familiar structure of a company. Imagine a workplace where every team member is not just an employee but an internal entrepreneur, driving innovation, and taking calculated risks to propel the organization forward.
This article delves into the core of intrapreneurship, unraveling its significance and impact on organizational dynamics. Join us as we explore how fostering an environment of innovation, granting autonomy to employees, and encouraging creative thinking can pave the way for transformative initiatives within the corporate sphere.
Understanding intrapreneurship
Intrapreneurship is the art of entrepreneurship within a company, where employees don the hat of entrepreneurs operating within the organizational structure. These individuals spearhead innovation, taking charge of products and services that shape the company’s future. Let’s delve into the profound impact of intrapreneurship on both business and individual career trajectories.
A glimpse into intrapreneurial history
The term “intrapreneurship” made its debut in 1979, gaining prominence through the publication of “Intrapreneuring: Why You Don’t Have to Leave the Corporation to Become an Entrepreneur” by Gilford and Elizabeth Pinchot. Time Magazine further thrust it into the limelight in 1985 with the article “Here Come the Intrapreneurs,” solidifying its place in corporate discourse. This concept, however, found its roots in the story of Art Fry at 3M in 1974, who, alongside Spencer Silver, birthed the iconic Post-it Notes.
 |  |
The cornerstones of intrapreneurship
At the heart of intrapreneurship lies the cultivation of autonomy and independence. This unique approach encourages employees to explore uncharted territories, experiment with novel ideas, and contribute to the continuous improvement of workflows. For instance, an intrapreneurial endeavor might involve researching and proposing more efficient workflow charts tailored to the company’s brand within a specific target demographic or devising strategies to enhance the overall company culture.
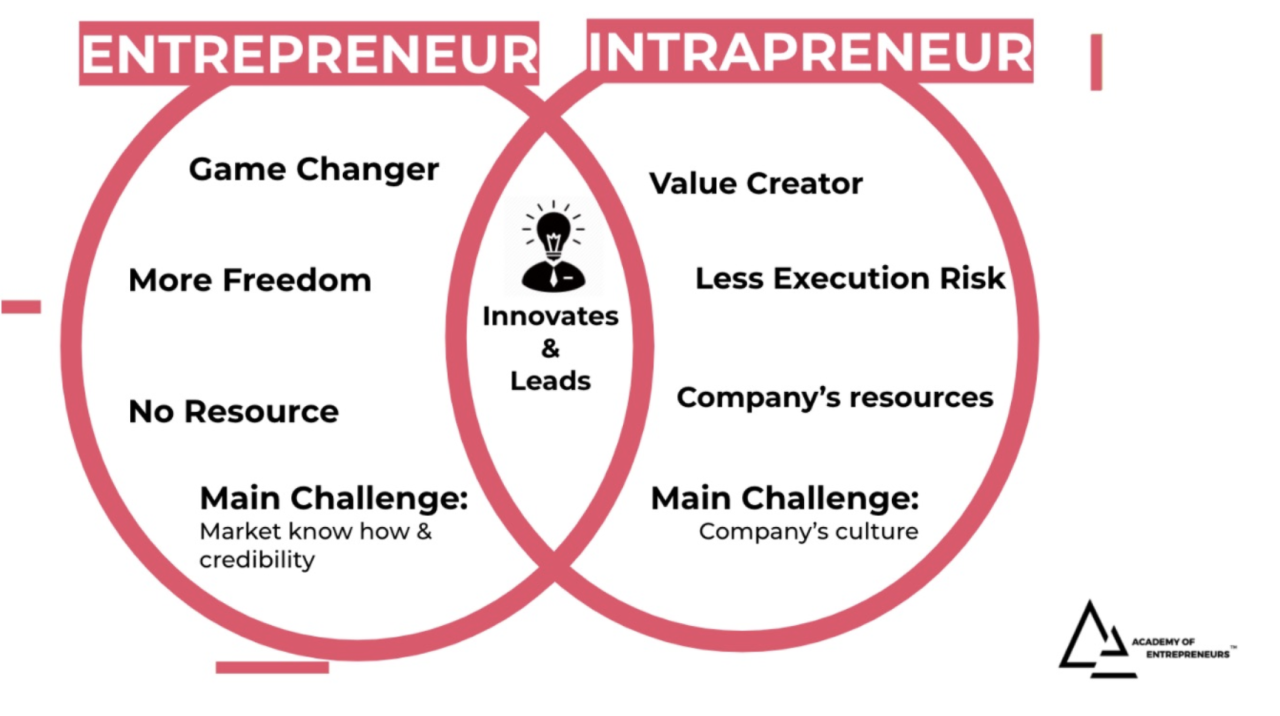
Intrapreneurship vs. entrepreneurship
While intrapreneurship and entrepreneurship share similarities, the fundamental distinction lies in the setting. Entrepreneurship thrives independently, detached from any organization, while intrapreneurship unfolds within established companies. This distinction grants intrapreneurs unique advantages.
Key advantages of intrapreneurship
- Access to resources: intrapreneurs leverage the company’s resources, tapping into financial support, industry connections, talent, and overall support, minimizing the fear of funding-related hurdles.
- Robust support system: in organizations fostering intrapreneurship, a robust support system is pivotal. This involves granting intrapreneurs the freedom to develop and implement their ideas, creating an environment where innovation can flourish.
- Mitigated risks: unlike entrepreneurs shouldering all risks, intrapreneurs benefit from the safety net provided by the parent company. This safety net significantly reduces the level of risk associated with their endeavors.
- Industry networking: intrapreneurs enjoy a head start in building industry connections, thanks to their roles within established companies. This networking opportunity provides access to valuable resources and experts.
Traits of successful intrapreneurs
- Innovators: successful intrapreneurs are perpetual innovators, constantly exploring new avenues for improvement and change.
- Problem-solvers: they excel at problem-solving, addressing challenges along the innovation journey with effective solutions.
- Risk-takers: embracing the inherent risks of innovation, successful intrapreneurs exhibit a calculated approach to risk-taking, understanding its integral role in the process.
- Opportunity seekers: with a keen eye for opportunities, intrapreneurs can identify situations as potential avenues for growth and innovation.
- Leaders: natural leaders, successful intrapreneurs inspire and lead by example, infusing enthusiasm and a hunger for innovation within their teams.
- Keen collaborators: understanding the power of collaboration, they actively encourage and embrace diverse perspectives, fostering a culture of teamwork.
How to implement intrapreneurship for organizations
Encouraging intrapreneurship within an organization requires a shift in mindset, an embrace of innovation, and a commitment to fostering a collaborative environment. Key steps include adopting an entrepreneurial mindset, embracing innovative ideas, encouraging collaboration, and providing the necessary support.
Benefits of Iintrapreneurship for businesses
- Spearheading innovation: intrapreneurs drive growth by leading innovation within companies, injecting fresh ideas and perspectives.
- Attracting top talent: an intrapreneurial culture attracts industry talents, creating a mutually beneficial environment where innovators flourish, and companies reap the rewards.
- Head start for employees: intrapreneurs, starting as regular employees, get a unique head start by building networks, gaining industry knowledge, and having access to experienced professionals.
- Building industry networks: innovators within established companies quickly build industry-wide networks, attending events and connecting with experts.
- Training ground for entrepreneurship: intrapreneurs acquire skills applicable to entrepreneurship, providing a learning ground for aspiring entrepreneurs.
Five steps to intrapreneurship for organizations
Enabling intrapreneurship within an organization requires a strategic and comprehensive approach. Here’s a concise blueprint encompassing five pivotal steps to cultivate an environment that nurtures and celebrates intrapreneurial spirit:
- Cultivate an empowering corporate culture:
- Objective: foster a workplace culture that empowers and encourages employees to explore, innovate, and contribute.
- Implementation: actively promote and communicate a culture that values initiative, creativity, and independent thinking. Encourage a mindset where calculated risks are seen as opportunities for growth.
- Establish clear measurement systems:
- Objective: define and communicate clear expectations, providing a roadmap for successful intrapreneurial endeavors.
- Implementation: develop transparent metrics and criteria for evaluating the success of intrapreneurial initiatives. Clearly outline what constitutes success, ensuring that employees have a tangible goal to strive for.
- Forge internal professional networks:
- Objective: facilitate collaboration and professional relationships among employees to amplify the impact of intrapreneurial efforts.
- Implementation: establish internal networks that encourage cross-departmental collaboration. Platforms for idea-sharing and collaborative projects can break down silos and create a conducive environment for intrapreneurs to thrive.
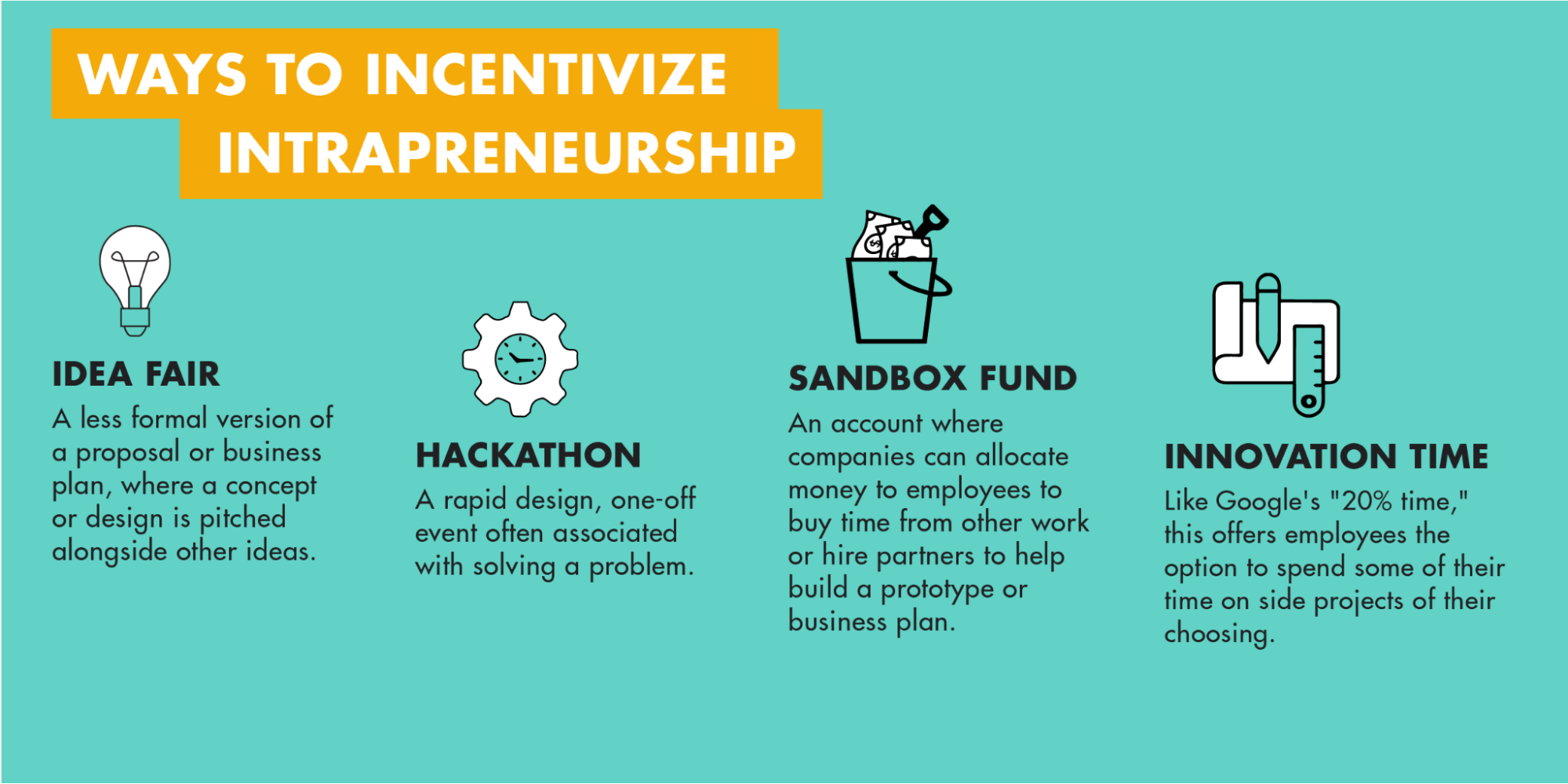
- Host innovation-centric events:
- Objective: promote innovation and provide a platform for intrapreneurs to showcase their ideas and skills.
- Implementation: organize seminars, workshops, and innovation boot camps that focus on fostering intrapreneurship. These events not only encourage ideation but also create opportunities for employees to stand out and be recognized for their innovative contributions.
- Assign mentors, not managers:
- Objective: provide guidance and support for new intrapreneurs, aiding their professional development.
- Implementation: designate mentors who serve as guides and advisors rather than traditional supervisors. These mentors should offer valuable insights, share experiences, and provide advice to intrapreneurs navigating the complexities of innovative projects.
Embracing intrapreneurship requires a holistic approach that encompasses cultural, structural, and support elements within the organization. By systematically implementing these five steps, companies can lay the groundwork for a dynamic and innovative workplace that not only values intrapreneurial initiatives but actively cultivates a culture where they can flourish.
Benefits of being an intrapreneur
Being an intrapreneur offers autonomy, opportunities for growth, a platform for innovation and creativity, a sense of purpose and fulfillment, recognition and rewards, and extensive networking and collaboration possibilities.
As we embark on this exploration of intrapreneurship, the doors to a world where corporate dynamics meet innovation swing wide open. Join us on this journey of creativity, risk-taking, and transformative success within the realm of intrapreneurship!
Conclusion
Intrapreneurship, far beyond a mere buzzword, guides organizations toward a culture of innovation and growth. Picture a workplace where every team member transforms into an internal entrepreneur, propelling the organization forward with a shared vision of change and calculated risk-taking.
Successful intrapreneurs possess traits like innovation, problem-solving, risk-taking, leadership, and collaboration. Neglecting intrapreneurship risks losing valuable contributors to other ventures. Organizations must foster a shift in mindset, encourage collaboration, and provide support. Becoming an intrapreneur involves deliberate steps like learning the innovation process, fostering teamwork, maintaining a passion for improvement, understanding business operations, and leveraging online courses. Being an intrapreneur offers a fulfilling role with autonomy, growth opportunities, and extensive networking possibilities.
If you want to reach new GEOs and audiences, maybe it is all waiting for you on Telegram? We’ve prepared some material about Telegram audiences. What are the messenger’s users like this year? How old they are, what they do, and what they are interested in!